Managers are vital to the digital transformation because they are the key to understanding and motivating healthcare professionals.
Need for leadership in the digital transformation

A study amongst almost 500 healthcare professionals and managers across Europe shows that there is a need for more leadership in the digital transformation. Biggest potentials and challenges are described below.
Biggest potentials
What are the biggest potentials for improving digital competencies of healthcare professionals? In the Erasmus+ project DELIVER, we have asked this question to almost 500 healthcare professionals and managers across Europe.
The answers show that the following aspects are very important:
- The role of the management and organization in facilitating why digital technology makes sense in order to change mind-set and attitude towards digital technology
- Creating better conditions for the healthcare professionals to get to know the new technology as well as reflect about their use of them
Biggest challenges
The DELIVER study shows that apart from access to well-functioning hardware and software/programs, which is a big problem in some countries, the biggest problems related to the use of digital technology in clinical practice are considered:
- Inadequate training with no clear structure, mainly due to lack of time and resources. As a manager put it: “The transition to digital technology was left somewhat to chance and therefore perhaps not included in programs, training and organizational plans”
- A widespread insecurity towards digital technology and the change it brings alongside a reluctance to replace the physical meeting with the citizen (patient) with digital technology.
This leads to the potential of many digital solutions not being exploited.
Changing mind-set and attitude
The biggest potential for improving digital competencies of healthcare professionals lies in changing the attitude and mind-set towards digital technology. The change should be towards more open-mindedness, curiosity and courage to try new solutions and workflows as well as better training in the use of existing digital technology.
The study also highlights that more active reflection on the value of digital technology as well as awareness of one’s shortcomings could improve the digital competencies of healthcare professionals – both in terms of being able to use the technology but also using it wisely.
Changes in mind-set and attitude and improved training in the use of digital technology go hand in hand. A manager says: “Employees must dare to embark on digital technology. If you have the will and the interest you will acquire the necessary competencies.” (Manager)
According to the DELIVER study, these two very closely connected areas of responsibility must therefore be the main priority of the healthcare managers in the digital transformation.
Source / References
Questions for reflection
- What do you see as the biggest challenges related to the use of digital technology in your work?
- What do you think is needed to strengthen the digital competencies of you and your colleagues?
- Do you recognize that mind-set towards digital technology and possibilities for training are the most important factors affecting the use of technology or do you see other central factors?
What we have learned
Implementing and working with technology takes time, practice and a change of mind-set because healthcare professionals are expected to adopt a form of digital literacy. Additionally, they must merge acquired digital competencies with their professionalism.
Supporting the digital healthcare professional – as a manager

Implementation of technology in healthcare places new demands on healthcare professionals. They are an important prerequisite for achieving the benefits of using digital technology, and often this requires new competencies and a changed understanding of the core task – both for the healthcare professionals and their leaders responsible for implementation.
Guide to support your digital co-worker
As a manager, you have a central role and responsibility in the digital transformation.
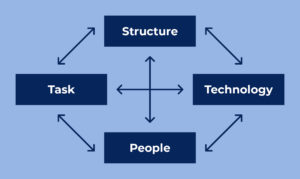
Using Leavitt’s diamond model as a framework, we can divide the responsibilities of the manager into 4 areas: technlogy, task, structure and people.
Technology
There are responsibilities related to the digital technology itself: purchasing, implementing, maintaining and updating hardware and software.
Task
Responsibilities for revising the tasks and workflows of the healthcare professionals so they match the new digital posibilities and expectations of the citizen (patient).
Structure
Responsibilities for creating the organizational structures necessary for a safe and efficient implementation of the technology: ICT support structure, cooperation with teachers or trainers and ICT departments, focus on data security and GDPR etc.
People
Finally, there are responsibilities related to the people; the healthcare professionals and the citizens (patients). This is about focusing on motivation, mind-set and attitudes towards digital technology, the psychological needs of the healthcare professionals and very importantly the needs and expectations of the citizen (patient).
This theme will primarily focus on responsibilities related to people and structure and less on technology and tasks.
Source / References
- Leavitt’s diamond model, The DELIVER project
Case: The struggles of a healthcare manager striving to promote digitization

In this case you will meet a health care manager, who is eager to support her colleagues in becoming digitally competent but faces challenges. The case is intended as a starting point for reflection on the role and responsibilities of the health care managers in supporting the health care professionals in the digital transformation. Read the case and reflect on how it relates to you as a manager.
It’s a busy day for Sarah, a healthcare manager at a bustling hospital. Sarah is very focused on supporting the healthcare professionals in her ward in utilizing digital solutions to enhance patient care and streamline processes. Sarah recognizes the presence of training and competency gaps among the healthcare professionals. She is quite aware that some individuals lack the necessary digital literacy skills or have limited experience with technology. Sarah understands that bridging these gaps is essential for successful implementation. Therefore Sarah is eager to provide training in new digital tools that have just been implemented at the hospital. But as so often before the hospital’s budget constraints and lack of staff pose a significant hurdle. She understands that without adequate resources, providing comprehensive training and support to the healthcare professionals will be an uphill battle.
As she navigates through the hospital, Sarah encounters resistance to change from some healthcare professionals. The introduction of digital solutions is met with skepticism and reluctance. Many professionals are comfortable with traditional methods and view the adoption of digital technology as a disruption to their established routines. Convincing them of the benefits and helping them embrace the new tools becomes an ongoing challenge for Sarah.
As the day progresses, Sarah finds herself grappling with the pressure to meet deadlines and deliver results. The fast-paced healthcare environment leaves little room for errors or delays. Balancing the urgency to implement digital solutions while providing sufficient training and support to healthcare professionals becomes an intricate juggling act for Sarah.
Questions for reflection:
- Do you recognize the dilemmas Sara is facing from your workplace?
- Which role do you see yourself in as a manager when it comes to the digital transformation?
- What do you see as your main responsibilities and challenges?
How to support healthcare professionals in using digital solutions

Here is the best advice from healthcare managers as well as teachers and professors in universities and hospitals on how to motivate and support healthcare professionals in using digital technology.
The results of research examining digital competencies amongst almost 500 healthcare professionals and managers (the DELIVER study) show a need for changing the mind-set of those working with the digital transformation as well as a need for better conditions for training of healthcare professionals’ digital competencies. So how do the healthcare managers succeed with this?
To help us answer this question, we have asked frontrunners in the digital transformation – doctors, nurses, teachers, professors and others – about their best advice to healthcare managers in this situation.
FIRST and foremost
The first and most important advice is to make sure the healthcare professionals are trained and are able to practice the use of new digital solutions. In many clinical settings this has not been a priority resulting in poor implementation and poor value of the digital technology. As said by a healthcare professional in the DELIVER project: “When we implement a new medical technology, we always make sure that staff is trained on how to use it. A new way of intubating a patient, new types of medication… Why do we not consider digital technology in the same way?”
WHAT digital technology to provide training on?
Only focus on technology that can be used today
One of the main advices is to only provide training in digital technology that can be used by the healthcare professionals in their daily work. Providing training in the use of technology, that are to be implemented weeks or months ahead is generally considered unsuccessful.
Make sure it works!
If the digital technology is flawed, not fully developed or not tested in the clinic there is a big risk that the training in the use of the technology will lead to even more reluctance, negativity and fear of the technology among the healthcare professionals. If possible, have the solution tested and further developed or develop useful guides for the use of the technology.
WHY is digital technology a good idea?
Research shows that healthcare professionals are generally driven by ‘public service motivation’. This motivation stems from the desire to do something good for others – for society as a whole or for special groups of citizens.
Therefore, to create motivation to use digital technology it is very important to focus not only on HOW the healthcare professionals should use the technology but also on WHY they should use it. Focusing on the advantages for the citizens and for the healthcare professionals themselves is a way to create motivation to accept change and dare try something new.
Sometimes the benefits and value for the citizen is not immediately evident to the healthcare professionals and must be highlighted. Many healthcare professionals prefer to have face-to-face meetings with the citizens as they consider this service to be of better quality than virtual consultations. However, as a managing neurologist asked:
Does the citizen prefer to sit at home surrounded by close family when receiving a diagnosis, OR to be in the hospital surrounded by clinicians in medical gowns? A freelance truck driver told his therapist that he would lose income and have to give up his house if he should go to hospital all the time for regular controls of his diabetes, so he preferred video consultations.
Helping the healthcare professionals understand the value of the technology is a main responsibility of the manager when introducing new digital technology.
The advantages of technology that healthcare professionals often highlight as particularly important are:
- Saved time
- Easier access to updated information
- Easier to share information
- Faster patient care
- More agile communication which support the healthcare professionals professionalism and promotes the opportunities to deliver high professional quality and service to the citizen.
HOW to use it?
Hands-on training
Over and over, the importance of practical hands-on training is highlighted by the managers. Introduction to the digital technology is important, but the curiosity, understanding and acceptance of the technology is closely connected to the practical hands-on training. This should preferably take place in the everyday clinical setting of the healthcare professionals. The advice is that the best results of the training are reached when it is carried out on-site where the clinical work is usually done. It is beneficial to involve the healthcare professionals in the planning of how to practice and use the technology. It may be necessary to differentiate the training between basic and advanced users of the technology.
Create possibilities to practice and share experiences
Create a stress-free environment where the healthcare professionals can feel free to make mistakes – without consequences for citizens (patients). Here, the healthcare professional can play around, make errors, press the buttons they don’t know and share experiences and reflections. Experience shows that it is often hard for the healthcare professionals to find the time to practice sufficiently to feel comfortable with the technology. It can therefore be a good idea to schedule one weekly hour of training and reflection in small groups for a specific period of time.
WHO should have responsibilities in teaching/training?
Teachers
The teaching/training of healthcare professionals in new technology can be organized in different ways. The teachers can both be external experts, a team in the hospital/unit who is responsible for training or local frontrunners who take the lead in training colleagues and spreading the good stories. It is a good idea to consider a combination of training from external experts who are specialized in the technology and employees who are close to the clinical practice.
Manager
Generally, there is an agreement that the manager should NOT be the day-to-day project leader in the implementation of digital solutions as the task is often time consuming and placed better elsewhere. Healthcare professionals who are motivated frontrunners and familiar with the clinical workflows are recommended to be in charge of the implementation of new technology and changed workflows as well as training activities.
The manager can support the digital training by setting up goals eg. Which tasks should we use the digital solution for, to which extent should we use the digital solution, who should use the solution, what are our milestones and deadlines?
The digital solution that is successfully implemented is the solution that is given attention repeatedly and where there is continuous focus and patience – even when the implementation is difficult and time consuming.
The manager can talk during staff meetings about the progress made through the use of the technology, invite healthcare professionals to reflect on the value of the solution and their use of it, say ‘good job’ when someone makes an effort to use it and reassure healthcare professionals that it is okay to make mistakes.
Support
Implementation is dramatically improved when support is easily accessible. Employees must have someone to help them and answer their questions when problems arise while using the digital technology. Easy access to support when it is needed is essential.
Support by an ICT department can be very useful for more general support, but the biggest success is seen when there is a possibility of support from local frontrunners, who know both the digital solutions AND the local workflows. They can help here and now when problems arise during a busy day.
Generally, close cooperation between the managers, the teachers and the ICT department is very important to ensure a successful implementation of digital technology.
Source / References
- The DELIVER project and Learnings from educational programme for management of the digitalized health care sector (‘Ledelse i et digitaliseret sundhedsvæsen’) by HR Ledelsesakademiet Region Syddanmark and Network of responsibles for training of digital skills of healthcare professionals in hospitals of Region of Southern Denmark



