There are many new terms to learn when speaking of the digital transformation and some of them appear to be almost the same or very similar.
Throughout all six themes, definitions will pop up to make sure that we have a common understanding of some focal terms. The following is a small selection to let you in on the basic terms.
We realize new ones will keep getting added to the extensive list, wherefore this will hardly be an exhaustive selection
Digital transformation

The adoption of digital technology by an organization to digitize non-digital products, services or operations. The goal for its implementation is to increase value through innovation, invention, customer experience or efficiency.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine is health services that are provided using information and communication technology, which replaces a physical meeting between the citizen (patient) and the healthcare professional who delivers the service. The first people to use video communication for medical purposes were clinicians at the University of Nebraska. In 1959, the university established a two-way television setup to transmit information to medical students across campus, and five years later linked with a state hospital to perform video consultations. (Read an extended definition of Telemedicine in Theme 4.)
Digitization/digitalization
Digitization is a technical process of converting analogue (including paper-based) health records to digital formats that may then be available for use electronically.
Digitalization is the integration of technology in the production of services. A process that involves the integration of digital technology into existing operations and tasks in public health/healthcare with the goal of improving efficiency and adding value to citizens (patients) and healthcare professionals.
The difference between digitization and digitalization: Digitization relates to the technical process of digital conversion, whereas digitalization refers to an organizational and cultural process of change in public health.
The integration of technology in the production of services.
A process that involves the integration of digital technology into existing operations and tasks in public health/healthcare with the goal of improving efficiency and adding value to citizens (patients) and healthcare professionals.
Digital health
The field of knowledge and practice associated with the development and use of digital technology to improve health.
Health technology
The application of organized knowledge and competencies in the form of devices, medicines, vaccines, procedures, and systems developed to solve a health problem and improve quality of lives.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine is defined as digitally supported health services where the citizen (patient) can avoid having to appear at the doctor’s office or at the hospital in cases where a physical appearance is not necessary for the consultation.
Telemedicine does not replace current medical practices but is a response to the challenges facing healthcare today: inequalities in access to care, changes in medical demography, geographical challenges of the system and economic constraints.
Digital Health Literacy
“The ability to seek, find, understand, and appraise health information from electronic sources and apply the knowledge gained to addressing or solving a health problem” [Norman and Skinner (2006)].
Digital competencies
Should be understood as the ability to combine digital technology, knowledge, competencies and attitudes appropriate to the context. Therefore, we divide the term into the following learning domains:
- Instrumental competencies to use digital tools and media.
- Knowledge, theories and principles related to technology.
- Attitudes towards strategic use, openness, critical understanding, creativity, responsibility and independence.
Source / References
- Schmarzo, Bill (31 May 2017). “What is Digital Transformation?”. Archived from the original on 2019-11-30. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- Wren, Hannah (1 December 2020). “What is digital transformation? Definition, Examples, Main Areas”. Archived from the original on 2020-12-02. Retrieved 9 October 2021
- 2020-12-02. Retrieved 9 October 2021 https://evisit.com/resources/history-of-telemedicine#:~:text=The%20first%20people%20to%20use,hospital%20to%20perform%20video%20consultations
- Iyamu, I., Xu, A. X. T., Gómez-Ramírez, O., Ablona, A., Chang, H. J., Mckee, G., & Gilbert, M. (2021). Defining Digital Public Health and the Role of Digitization, Digitalization, and Digital Transformation: Scoping Review. JMIR public health and surveillance, 7(11), e30399. https://doi.org/10.2196/30399Global strategy on digital health 2020-2025. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- https://joint-research-centre.ec.europa.eu/digcomp/digcomp-framework_enWorld Health Organization. (2011). Health technology assessment of medical devices.#11 HTA Advancement-FINAL.indd (who.int)
Digital health
The field of knowledge and practice associated with the development and use of digital technology to improve health.
“The ability to seek, find, understand, and appraise health information from electronic sources and apply the knowledge gained to addressing or solving a health problem” [Norman and Skinner (2006)].
Health technology
The application of organized knowledge and competencies in the form of devices, medicines, vaccines, procedures, and systems developed to solve a health problem and improve quality of lives.
What are digital competencies for healthcare professionals?

What do we mean, when we say digital competencies for healthcare professionals and what are the potentials for improving digital competencies for the healthcare professional?
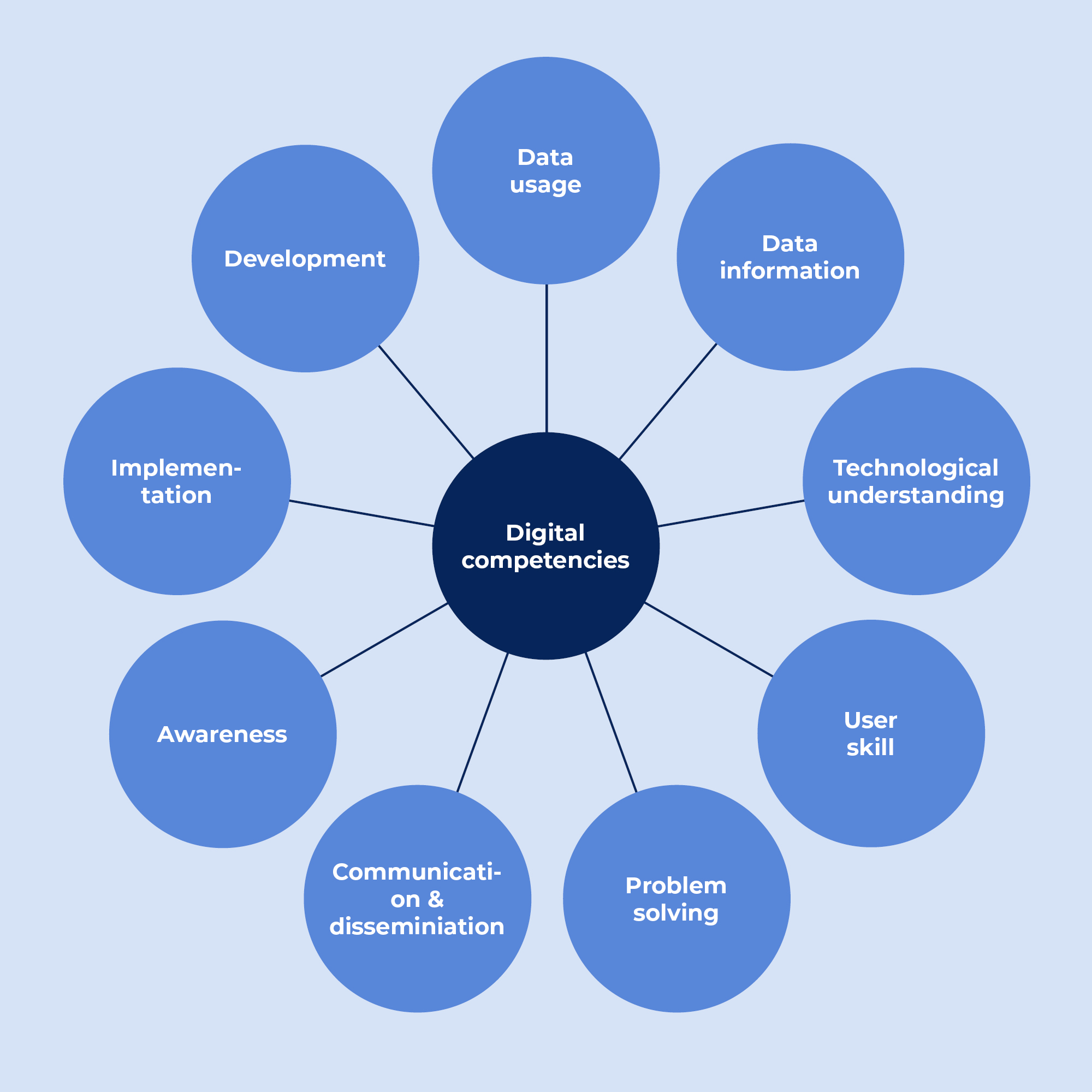
Digital competencies for the healthcare professional
The DELIVER study has shown that employees generally see digital competencies as being able to use and apply digital technology.
The model shows which digital competencies were highlighted in the DELIVER study as particularly important for the healthcare professional. These are:
- Data usage
- Data information
- Technological understanding
- User competencies
- Problem solving
- Communication & dissemination
- Awareness
- Implementation
- Development
Potentials for improving digital competencies
Based on the DELIVER study, the following were suggested as areas that have potential for improvement in regards to digital competencies for the healthcare professional.
- Change of attitude and mind-set in relation to technology towards more open-mindedness, interest, curiosity, patience and courage.
- More reflection on value of technology and awareness of one’s shortcomings.
- Skills to use existing digital tools and further training in communicating digitally and training colleagues and citizens (patients) in using digital solutions.
- Technological understanding and trouble shooting.
Source / References
Potentials and challenges for the digital healthcare professional

In general, digitization is viewed as leading to greater flexibility, better working conditions, increased research and most importantly: an increase in the quality of care. However, the digital transformation triggers radical changes in the daily routines of nurses, therapists and other healthcare professionals. These are the conclusions of the DELIVER need assessment study (IO1).
Digital transformation is seen as inevitable by healthcare managers and generally leads to a better healthcare system with more efficient workflows and better services for citizens (patients). Especially when considering a future with a smaller workforce and more complex issues.
However, if you ask the healthcare professionals they feel a lot of work goes to waste in the process due to the cost of making changes.
Challenges of digital technology
The DELIVER quantitative survey shows that digitization are perceived as leading to following challenges:
- More administration and registration, which takes time away from the citizen. In some cases this impairs the relation between the healthcare professional and the citizen.
- Digital technology can give cause to resistance as many healthcare professionals experience a bigger burden with new technology, changing workflows etc.
- The majority of healthcare professionals do not exploit the full potentials of their digital systems. There is still a lot of double registration work (digital and paper), lack of integration between systems preventing the flow of information.
Potentials of digital technology
The health care professionals and health care managers in the DELIVER study point at following as the biggest potentials of increased digitization:
Most significant advantages:
- Faster and easier access to up-dated information due to uniform and centralized digital documentation
- Ability to share information across providers through shared systems and integrate data for a better overview
These advantages create:
- Optimization of time for health care professionals and faster patient care of improved quality and with a higher data security.
Other advantages:
- Agile, personalized and accessible communication
- Order, transparency as well as improved legal compliance.
- Systematic collection of data accessible for research.
- Automation of routine tasks for smarter use of resources and less human mistakes.
Case example: Nurse Sarah’s Day: Balancing the Impacts of Digitization
Nurse Sarah starts her day at the busy hospital, ready to tackle a series of tasks.
Entering Room 205, Nurse Sarah greets Mr. Johnson, an elderly patient with a kind smile. She takes a seat next to him and engages in a conversation, attentively listening to his concerns. With her tablet in hand, Nurse Sarah efficiently retrieves his digital health records, reviewing his medical history and recent test results. This quick access to up-to-date information allows her to tailor her questions and provide a thorough assessment of his condition.
After the conversation, Mr. Johnsons takes a rest in his patient bed and Sarah continues documenting the details of the consultation, capturing vital information and updating treatment plans in the digital documentation system. Sarah understands the importance of maintaining accurate records accessible to her colleagues across sectors, ensuring continuity of care.
After a short lunch break, Sarah prepares for Mr. Johnson to be discharged from the hospital. Gathering necessary information, she ensures a seamless transition of care. Utilizing the integrated communication system, she sends messages to the private practitioner, the patient transportation service and the nurse who is visiting Mr. Johnson in his home the following day. These messages provide updates on patients’ conditions, test results, and any relevant instructions. The secure and efficient exchange of information allows for effective collaboration and smooth transitions, ensuring the best care for patients.
Amidst her tasks, Sarah encounters both positive and negative aspects of digitization. The ability to access patient information quickly and easily empowers her to deliver personalized care. However, she also experiences the challenges of increased administrative tasks and the adjustment to new technologies and she often has a feeling of distance to the patients when meeting them on a screen instead of in a physical meeting.
Source / References
Questions for reflection
Think about the changes which digital technology has caused at your work the last year, 5 years and 10 years:
- Which challenges have you faced do to the new technology?
- How have you overcome these challenges?
- Which positive implications has the digital technology had for you and your collegues?
- Which potentials and challenges do you expect from increased digitization in the health care sector?
- How do data security and privacy policies impact the adoption and utilization of digital solutions in healthcare, and what are the implications for accessing and sharing information?



